Price Slices - Premium Feature
Price Slices
Price Slices allow users to view theoretical outcomes of option positions, while providing the flexibility of changing data points, such as entry price or what the results will be if the stock price moves a specific dollar or percentage amount.
This feature is helpful with building discipline on when to exit a trade if it goes against you.
This feature is accessible when using the Strategy Templates on the Research>Option Tab
The default starting points include:
- Entry Point – shown in Blue in our example.
- High Point – considered Target or Resistance point – shown in Green.
- Low Point – considered Stop or Support point – shown in Red
(Up to 7 Price slices can be added for additional evaluation. See below for more details)
On Research>Option Tab, click the down arrow next to the default “Call+Put” view in the upper left corner of the window to access the Strategy Templates:
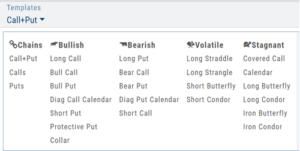
Select your Strategy and set up the position:
Quantity, Expiration Date, Strikes
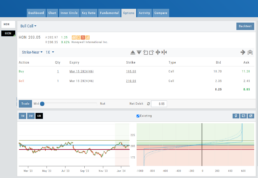
On the right side of the same screen, click the ![]() button to display the default settings.
button to display the default settings.
Using our example:
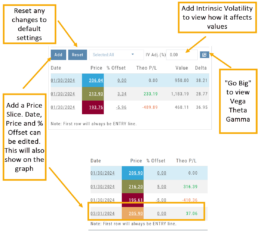
Entry point is $206.04 (Current Stock Price) shown in Blue
High point – defaults to 5% above Entry: $216.34, shown in Green/Gold
Low point – defaults to 5% below Entry: $195.74, shown in Red
The values are for ‘today’: what the Profit or Loss would be if the stock price were the High or Low price.
The Date, Price and/or % Offset can be manually adjusted, as indicated by the underline – to view different scenarios.
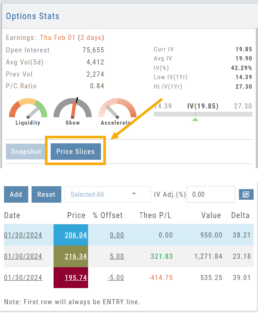
Price Slices – Adjust the % Offset Value
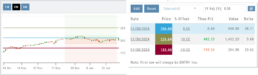
% Offset values were manually changed to 10% and -10%.
The lines on the graph are dynamically updated
Price Slices – Adjust the lines
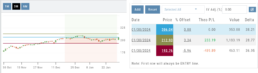
In this example, the Top and Bottom lines were adjusted on the graph itself.
The new placement dynamically updated the values on the right.
Price Slices – Add, Reset, Go Big
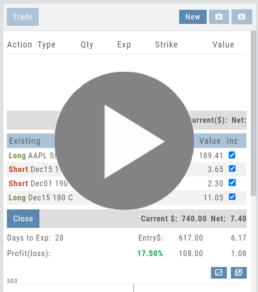
Multiple Position Analysis
We often have more than one position on a particular Stock/ETF, so how can each position, or leg be evaluated?

Fundamentals Tab
Fundamentals
Fundamentals provide valuable insights into the financial health and performance of a company. They offer a comprehensive analysis of the company’s operations, profitability, growth potential, and overall stability.
Fundamentals are comprised of Earnings, Dividends, Price Projections, Profitability, Growth, and Cash Flow.
Profitability, Growth, and Cash Flow offer even more detail. Either click the button in that section:
![]()
OR click the appropriate category at the top of the window:

Earnings data provide insight into a company’s financial health and performance.
Past earnings reports offer insight into the company’s historical growth, profitability, and stability. Positive earnings trends may indicate a well-performing company. Negative or declining earnings could be cause for concern.
Earnings
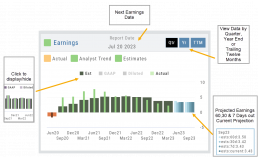
Earnings projections provide forecasts of a company’s future earnings to gauge Market sentiment and investor expectations. Projections are compiled by financial analysts using factors such as industry trends, company guidance, and economic conditions. Surpassing or falling short of projections can greatly impact stock price.
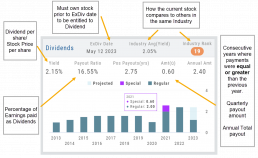
Some benefits to both the company and shareholders include:
Income Generation
Shareholder Loyalty
Return on Investment
Dividend Reinvestment
Signal of Financial Health
Possible Tax Advantages
Disciplined Capital Allocation
Dividends
The decision to pay dividends is up to the company’s management and board of directors, who weigh various factors, including the company’s financial position, growth prospects, and other capital allocation priorities. Dividend payouts are not guaranteed and may fluctuate or be suspended based on the company’s circumstances and strategic considerations.
Price Projection
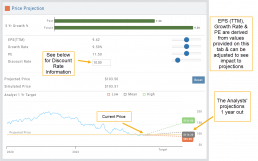
Discount Rate
Determining the appropriate discount rate for a stock is a subjective process and depends on various factors.
Here is an example:
- Risk-Free Rate: Start by considering the risk-free rate, (the theoretical rate of return on a risk-free investment such as government bonds). This serves as a baseline for the discount rate. An online search can locate this information for you.
- Risk Premium: Assess the risk associated with the specific stock you are evaluating. Stocks are inherently riskier than risk-free investments, so you need to add a risk premium to the risk-free rate. The risk premium accounts for the additional return expected by investors for taking on the extra risk. The risk premium can vary depending on factors such as industry, company-specific risks, economic conditions, and market volatility.
- Beta: This measures its sensitivity to market movements.
Beta of 1 = the stock moves in line with the overall market
Beta > 1 = the stock has higher volatility and would warrant a higher discount rate to reflect the increased risk. - Company-Specific Factors: Are there unique company factors (financial health, competitive position, growth prospects, management quality, etc) that could positively or negatively influence the discount rate?
- Sensitivity Analysis: Changing the discount allows you to assess the impact of the stock’s valuation. Some sectors are subject to more volatility than others: the Energy and Material Sectors tend to be more volatile than Consumer Staples or Utility Sectors.
The discount rate is subjective. Different investors might have different views on what the appropriate discount rate is for a given stock, based on their own risk tolerance, the specific risks associated with the company, and their expectations for future market conditions.
Profitability
Revenue: Money generated from sales of goods or services. It is income earned prior to deducting expenses or costs
Cost of Revenue: Expenses directly related to production, manufacturing, or acquisition of products/services sold. Typical examples include raw materials, labor, overhead, etc.
Operating Expenses: Day-to-day, necessary operating expenses not directly related to the production/acquisition of goods/services. Examples: Wages, utilities, depreciation, advertising, etc.
Other Expenses: Depending on the nature of the business can include: Taxes, Interest, Non-operating losses, Restructuring, Non-recurring, etc.
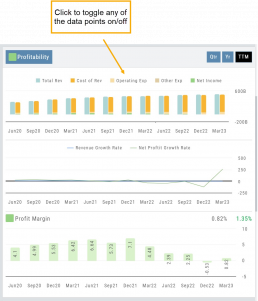
Revenue Growth Rate: Percentage change (+/-) in a company’s sales/revenue over a period of time:
Revenue Current–Revenue Previous/Revenue Previous x 100
Net Profit Growth Rate: Percentage change (+/-) in a company’s net profit over a specific period of time:
Net Profit Current–Net Profit Previous/Net Profit Previous x 100
Profit Margin: Percentage of revenue a company retains after deducting all expenses.
A higher profit margin indicates a company is generating more profit relative to its revenue. A lower percentage suggests higher expenses in proportion to revenue.
Growth
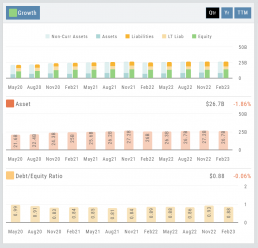
Asset: These can vary by industry/company. Common examples that contribute to a company’s growth are Financial, Intellectual Property, Human Capital, Physical Assets, Technology/Info Systems, Customer Base, Brand Equity, Partnerships, and Networks.
Debt/Equity Ratio: Total Debt divided by Total Equity. Interpretation varies by industry and a company’s specific circumstances: a high ratio can indicate higher financial risk OR effective management of debt through cash flow. A low ratio can indicate a conservative financial position OR under-utilization of debt and missed opportunities for growth.
Non-Current Assets: Resources not intended to be converted into cash or used up within a year.
Assets: Anything of value that has the potential to generate future economic benefits.
Liabilities: Obligation or debt a company owes to external parties that must be fulfilled in the near future.
Long-term Liabilities: Obligation or debt a company owes but has more than a year to repay.
Equity: The portion of a company’s value belonging to its owners or shareholders after all debts and obligations have been settled
Operating Cash Flow: Represents the cash inflow/outflow directly related to day-to-day activities including sales of goods and services, paying operating expenses, and collection of receivables.
Free Cash Flow: Cash flow available for discretionary use after accounting for operating expenses, capital expenditures, and changes in working capital. Positive values offer opportunities, negative values may indicate financial challenges.
Cash Flow
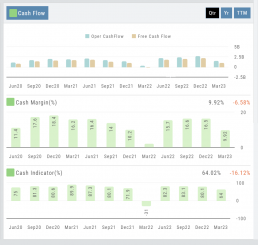
Cash Margin %: Percentage of cash generated from a company’s sales revenue after deducting its cash operating expenses. It measures the profitability and efficiency of a company’s operations to generate cash.
Cash Indicator: The industry percentile ranking of a company’s ability to generate cash from its operations.
Price Change Indicator
Green and Red Arrows have been added to each symbol tab when in Research.
This applies to any selected Watchlist or the default “Recents” list.
Each time one symbol is clicked, the entire list will update the latest price update.
Customize Watchlist Views
Customize Watchlist Views
You have the ability to customize Watchlist Views – based upon criteria you want to see.
Click on the ![]() next to “Default” or current view you are on to create a different View.
next to “Default” or current view you are on to create a different View.
If/When you want to edit any of your personal views, simply click the ![]() icon, remove/add criteria, adjust placement, then click “Save”.
icon, remove/add criteria, adjust placement, then click “Save”.
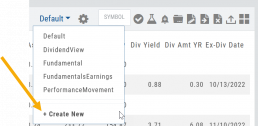
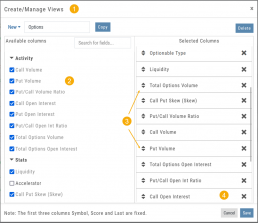
From Assets to Z-Score, there are over 160 data points to select from including data from: Company Information, Technicals, Valuation, Fundamentals & Options.
Simply:
1. Name the View
2. Select Data Points
3. Arrange – clicking on arrows to move up/down
4. Save
Your Watchlists are now more powerful because they show the data you want to see to help you make your trade decisions.
The Result:
Note: The Symbol, Score Icons and Last Price are fixed
Research Your Watchlists
Research Watchlist Functionality
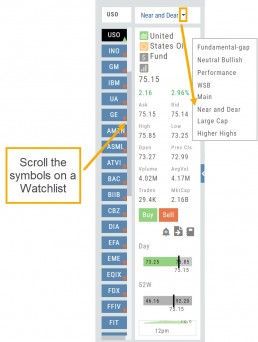
Users are able to access all Watchlists from the Research Tab.
Click the ![]() to access the dropdown list as shown in the graphic.
to access the dropdown list as shown in the graphic.
Lists with more than 20 symbols will have a scroll bar allowing for easier research of larger lists.
All other functionality remains the same: Symbols can be moved to other lists, have alerts set, deleted, add Journal notes
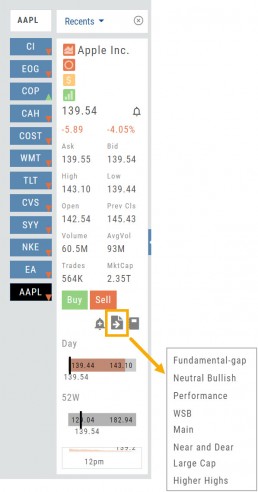
When a symbol is entered in the Symbol Search Box on the Research Tab, the symbol will automatically be displayed on the default “Recents” list.
In addition, when a symbol or group of symbols is sent to Research from anywhere else on the platform, it will appear on a list under the default “Recents” list.
Examples of when the “Recents” list will be displayed:
- Sending a symbol/symbols from a list on a Watch Tab.
- Selecting a group of symbols from a Scan or Screener list.
- Clicking on the Technical Icon from any symbol when not in the Research Tab. will be displayed under “Recents”.
The functionality of adding a note, an alert or sending a symbol to a specific list remains the same.
Option Chain Functionality

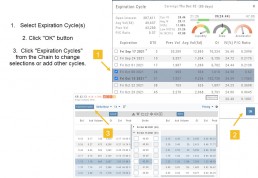
Research>Option Tab, click on “Expiration Cycle” for the “Call+Put”, “Calls” or “Puts” view.
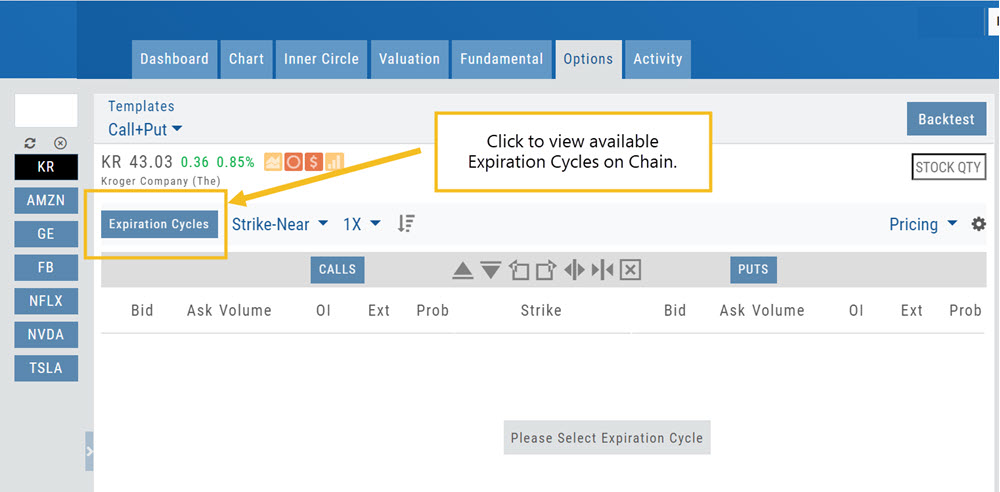
Option Chain Expiration Cycles
The Option Chain Expiration Table gives you control of selecting which Expiration Cycle(s) you want to view.
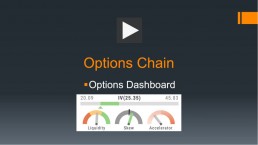
The Option Dashboard provides a wealth of pertinent information to make informed decisions easier.
See below for more detail
Expiration Cycles: All available options will be displayed. Monthly Options are indicated with an asterick![]()
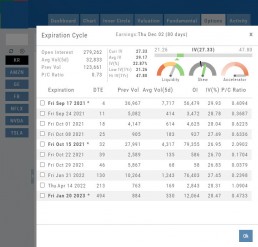
Select Expiration Cycles
Click ‘OK”
Chain will display for selected